—— Notes on CH8 Haskell, Seven Languages in Seven Weeks by Bruce A. Tate
引言
Haskell不同于Scala,是一门纯函数式语言,它强制使用者使用函数式语法而没有妥协。
-
是一门强类型定义的静态类型语言。它的**类型模型基于推断理论(in-ferred)**并被公认为是函数语言中最高效的类型系统之一。你会发现该类型系统支持多态语义并有助于人们作出十分整洁清晰的设计。
-
支持Erlang风格的模式匹配(pattern matching)和哨兵表达式。你也能在Haskell中发现Clojure风格的惰性求值(lazyevaluation)以及与Clojure和Erlang相同的列表推导语法。
-
无副作用,通过monad概念保存状态:一个Haskell函数可以返回一个有副作用并且会被延迟执行的结果.
Day1 逻辑
在OS X下安装Haskell环境:brew install haskell-platform
通过命令启动交互式环境:ghci
基本类型
1 | {- basic type -} |
D2 函数
定义
1 | {- let binding -} |
1 | {- ./double.hs -} |
递归
1 | Prelude> let fact x = if x == 0 then 1 else fact (x - 1) * x |
使用Tuple
1 | {- ./fib_recusive.hs -} |
1 | {- ./fib_tuple.hs -} |
1 | {- ./fib_pair.hs -} |
遍历列表
通过let (h:t) = list
1 | {- ./fib_pair.hs -} |
生成列表
1:[2,3,4] -> [1,2,3,4]
偶数列表
1 | module Main where |
Range
1 | [1..10] |
List Derivation (like python)
1 | [x * 2 | x <- [1,2,3]] |
练习 乘法表
1 | module Main where |
Day2
高阶函数
匿名函数
1 | (\param1.. paramn ->function_body) |
map
1 | map (\x -> x * x) [1, 2, 3] |
filter、foldl和foldr (reduce)
1 | Prelude> filter odd [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] |
where
1 | {- haskell/map.hsmodule -} |
柯里化
把多参数函数,拆分成多个只有一个参数的函数
1 | Prelude> double x = x * x |
惰性求值
一个无尽序列
1 | {- my_range.hs -} |
惰性 Fib 数列
1 | {- lazy_fib.hs -} |
Day3
类与类型
自定义类型
1 | {- cards.hs -} |
多态函数
1 | backwards :: [a] -> [a] |
多态数据类型
类型相同的三元组
1 | module Main where |
树
1 | module Main where |
类
非面向对象的类概念,它不涉及数据,可以精细控制重载和多态。
以下是 Eq 类的定义:
1 | class Eq a where |
类支持继承:
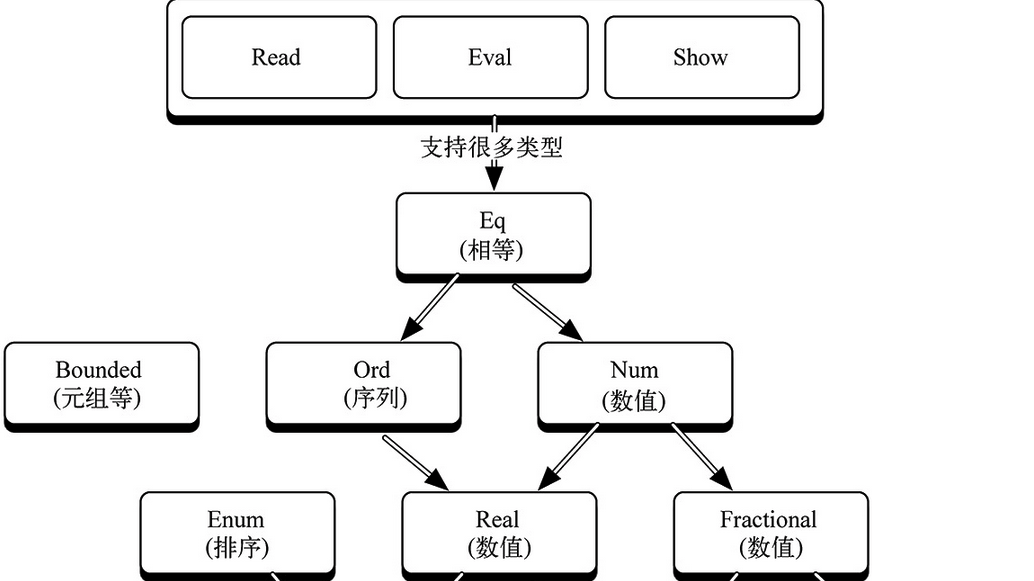
Monad
海盗寻宝问题
Python Approach
1 | def treasure_map(v): |
Functional Approach
1 | module Main where |
Let-in Approach
1 | module Main where |
Monad Approach
1 | module Main where |
More Monad
do Sugar Syntax
1 | module Main where |
Definitions of return and bind(>>==)
1 | instance Monad [] where |
Crack Password
1 | module Main where |
Maybe Monad
Maybe 能够解决一些函数返回失败,如数据库、网络、文件I/O等函数。
下面是 Just 定义:
1 | {- Just 类似 Swift 的 Optional-} |
进入正题,处理HTML文档,不用 Maybe Monad 时需要处理每层(paragraph / html / body)的 Nothing 异常:
1 | {- Without Maybe Usage-} |
用 Maybe Monad :
1 | {- Maybe Usage-} |
